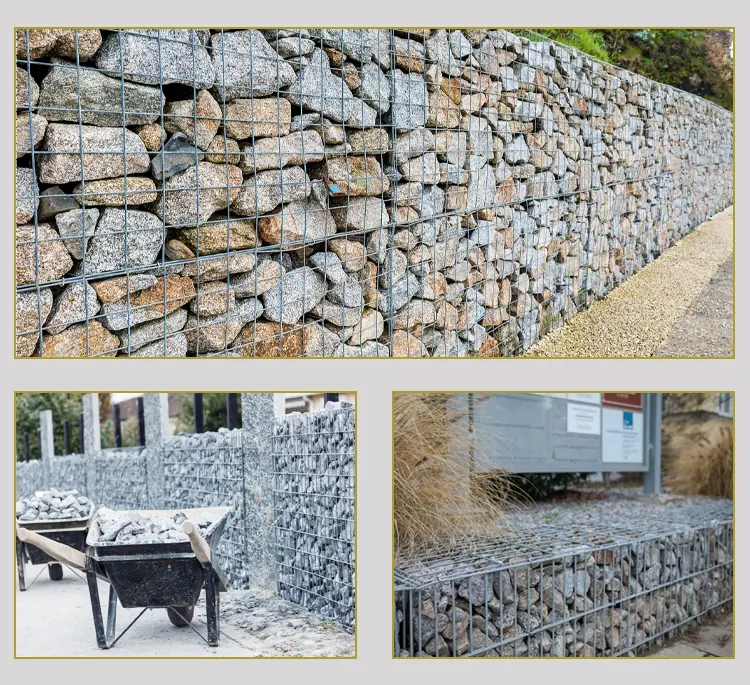
What Is the Difference Between Wire Mesh and Weld Mesh?
In the fencing, construction, and industrial materials world, the terms wire mesh and weld mesh often appear together. Many people assume they are interchangeable, but in reality, the two materials are engineered in different ways and perform differently in long-term applications. Understanding these differences helps you choose a mesh that truly matches the demands of your project.
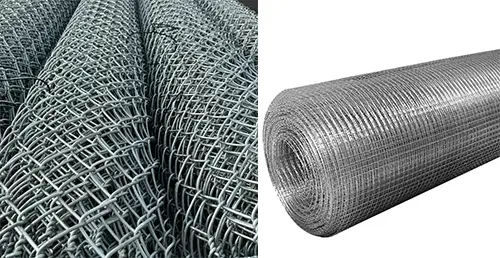
1. Structure and Manufacture
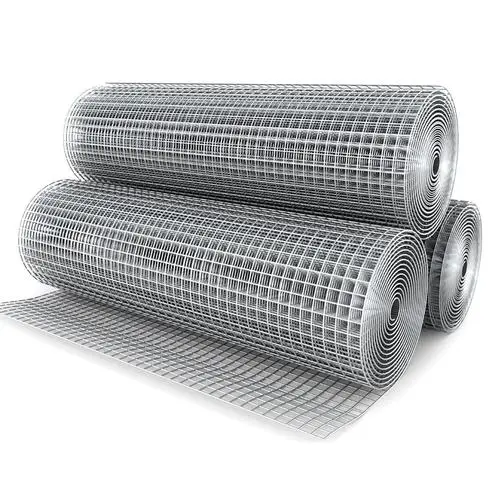
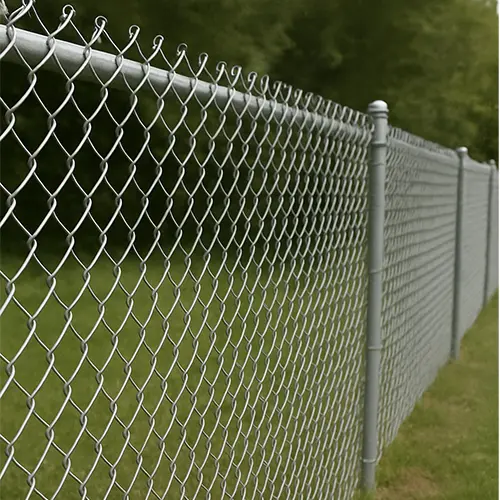
Wire Mesh (Woven Wire Mesh)
Wire mesh is produced through a weaving process. Horizontal and vertical wires interlace to form openings, similar to textile manufacturing. Because the intersections are not fused, the mesh has a natural flexibility.
This woven structure allows for high precision in opening size, making it suitable for screening, sieving, insect protection, and filtration where accuracy matters.
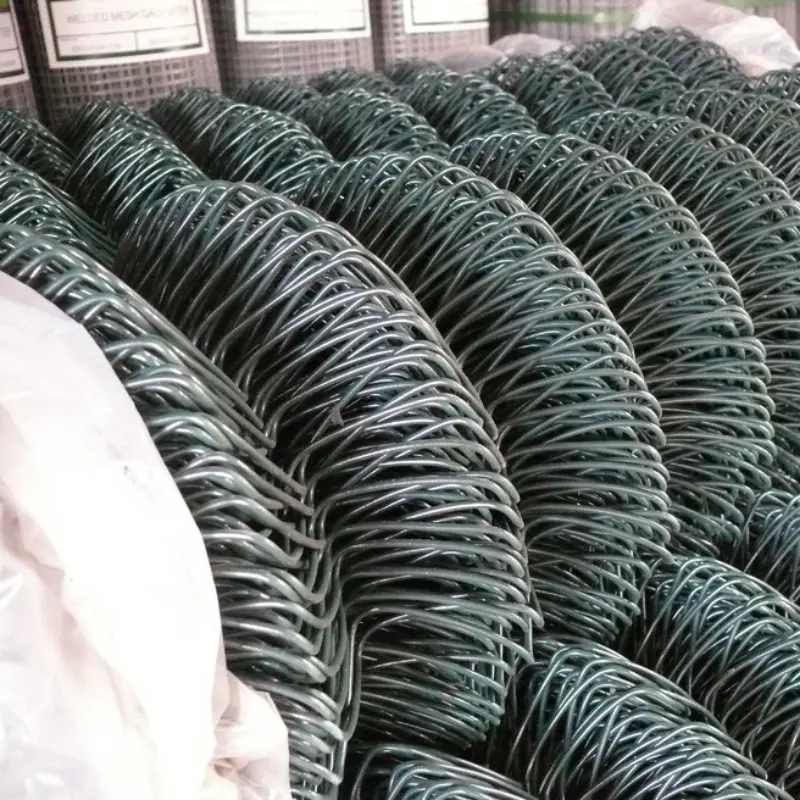
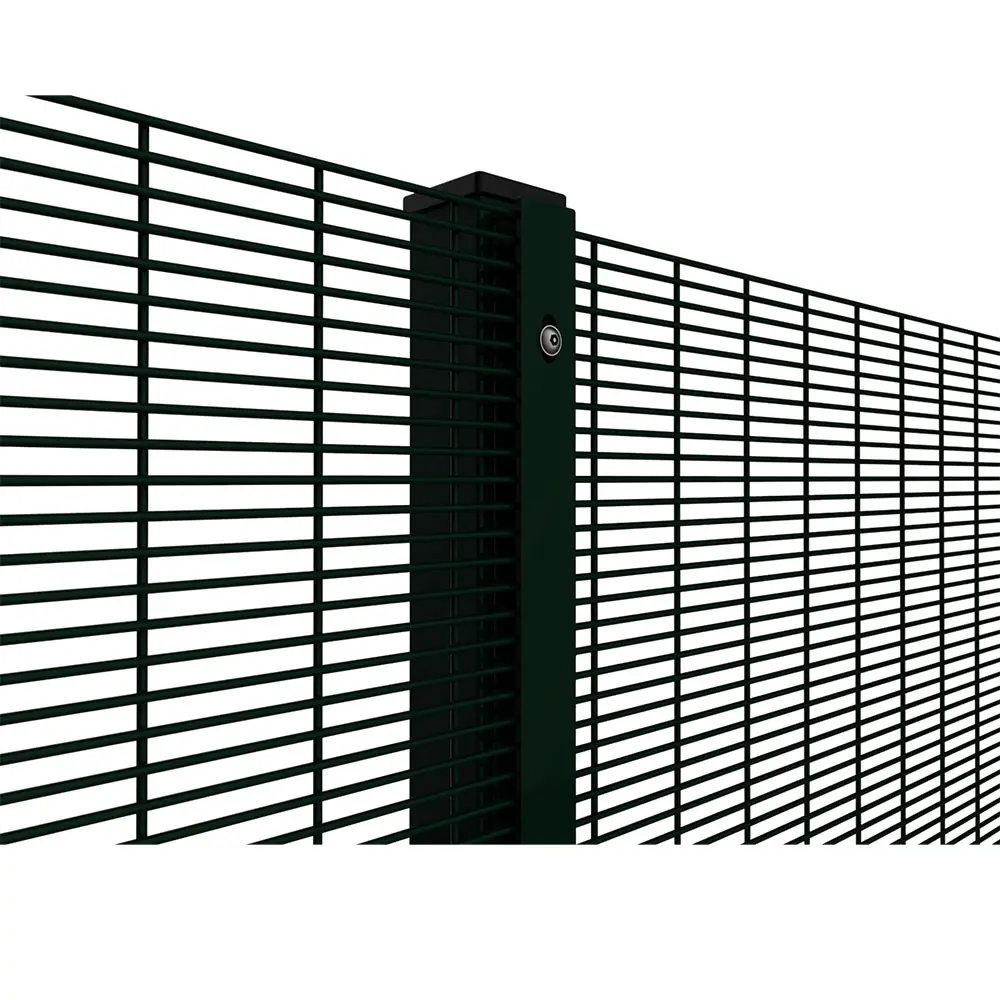
Weld Mesh (Welded Wire Mesh)
Weld mesh is made by spot-welding wires at every intersection. Each joint becomes a rigid connection, creating a grid that maintains its shape under stress.
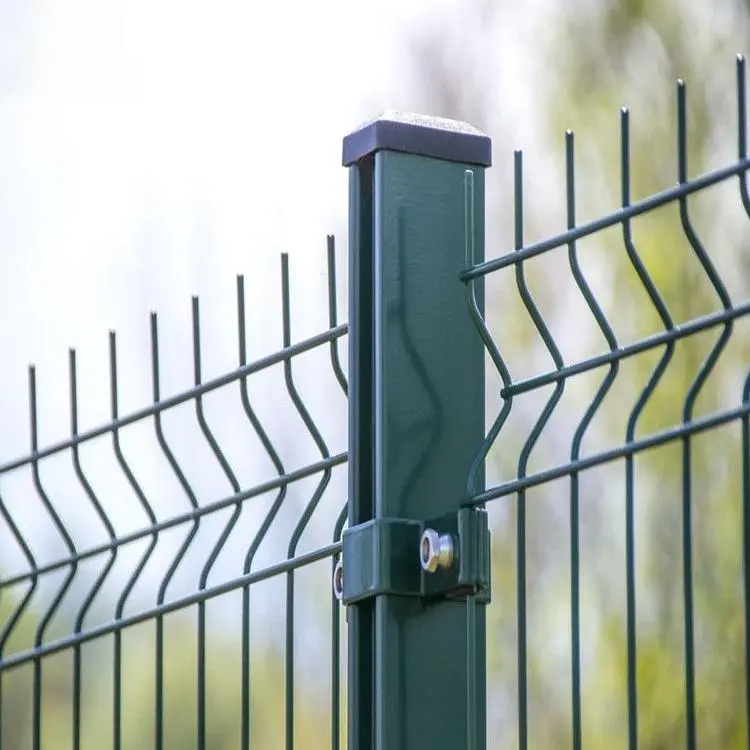
The welded bonds provide uniform openings and excellent strength, which is why this type of mesh is widely used in fencing, reinforcement, cages, and industrial safety barriers.
2. Strength and Mechanical Behavior
Weld mesh is built to stay rigid. The welded intersections prevent sliding or distortion, allowing the mesh to resist impacts, bending, and pressure.
Wire mesh, by contrast, has no fixed joints. It can flex, drape, or be shaped more easily, but it will not provide the same level of structural strength.
Because of this, the two materials serve different roles in practical engineering—one prioritizes stability, the other adaptability.
3. Flexibility and Workability
If your application requires bending, forming, rolling, or shaping the mesh, woven wire mesh performs better. It behaves almost like metal fabric, especially in finer gauges.
Weld mesh is more resistant to deformation. Even when supplied in rolls, its stiffness is noticeable, which is also what makes it reliable for load-bearing or protective installations.
4. Material Cost and Practical Selection
Wire mesh can be more expensive in fine weaves or when high precision is required. Weld mesh is usually more cost-efficient for large panels, fences, and structural uses.
So the choice is rarely about which one is "better," but about what the project demands: accuracy and flexibility, or strength and stability.
5. Typical Applications
Wire Mesh Is Often Used For:
-
Filtration and sieving
-
Industrial screening
-
Insect protection
-
Fine particle separation
-
Light-duty protective coverings
Weld Mesh Fits Applications Such As:
-
Security fencing and perimeter control
-
Animal cages and agricultural enclosures
-
Construction reinforcement
-
Machine guards and industrial barriers
-
Storage partitions and shelving
Each type has its place, shaped by how it is manufactured and how it behaves under load.
By looking at how the mesh is made, how it performs mechanically, and where it is applied, the differences between wire mesh and weld mesh become clear. Once you match these characteristics to the needs of your project, the choice tends to reveal itself naturally.











