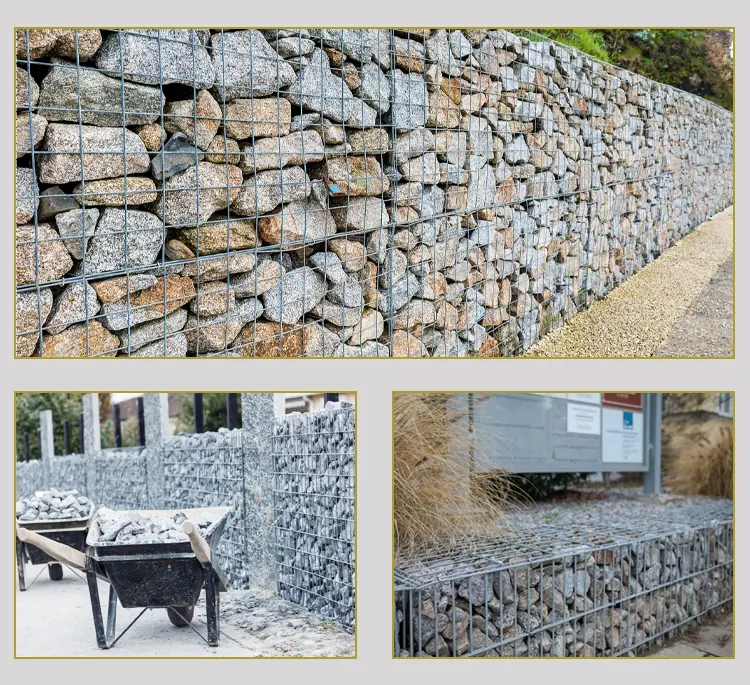
Razor Wire vs Barbed Wire
When it comes to perimeter security, barbed wire and razor wire are two common choices used around the world. While they may look similar at first glance, they serve different purposes, are constructed differently, and offer varying levels of security. In this blog, we'll break down the key differences between barbed wire and razor wire.
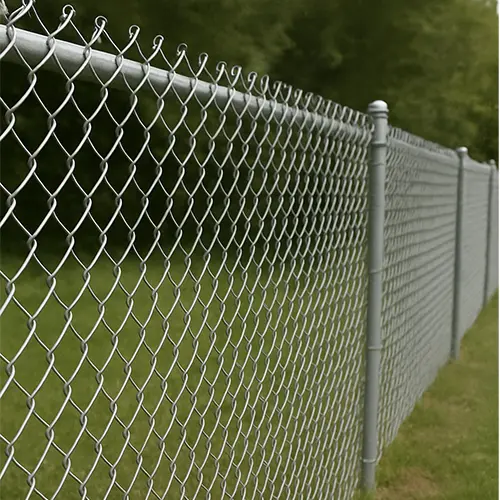
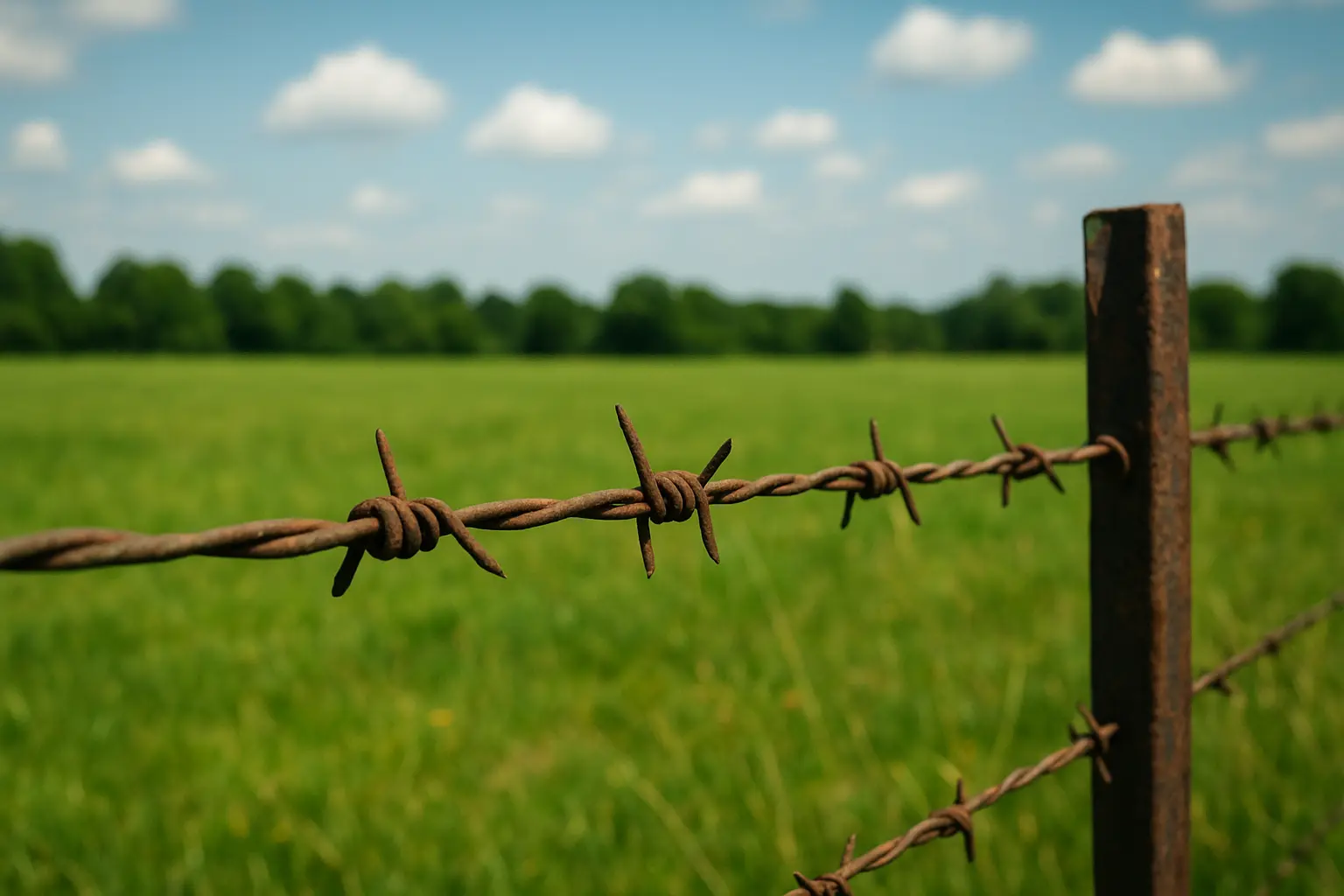
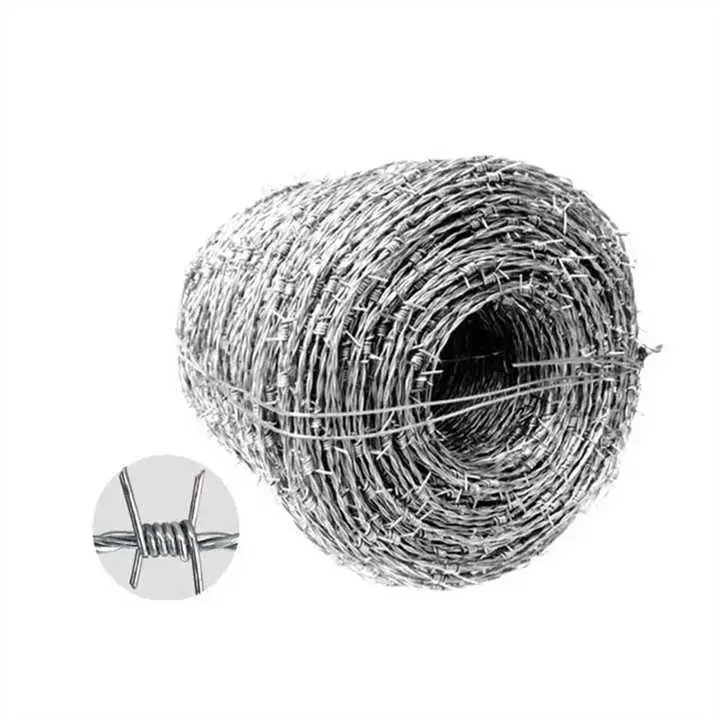
Barbed Wire
1-Construction
•It comprises one or two primary longitudinal strands, typically twisted steel wire, onto which sharpened metal barbs are periodically affixed. Barbs are formed by cutting and bending the wire into pointed projections.
•Barb placement follows are regular spacing pattern along the strands (e.g., intervals of 4-6 inches).
2-Functional Mechanism
•Primarily functions as a deterrent and a marginal physical barrier—contact results in discomfort, superficial lacerations, and entanglement of garments or skin, complicating traversal efforts.
•Demonstrates high efficacy in livestock containment(cattle, horses), where animals learn avoidance behavior.
•Serve as a psychological deterrent to human intruders.
3-Security Efficacy Against Human Intrusion
•It has a moderate deterrence level. The determined individuals can often overcome this barrier relatively rapidly, accepting risks of minor injury and material damage.
4-Typical Applications
•It's used for correctional facilities, military installations, national borders, critical infrastructure (e.g., power generation plants), sensitive government sites, and secure storage complexes.
5-Morphological Characteristics
•It presents as linear wire strands featuring periodic protruding sharp points.
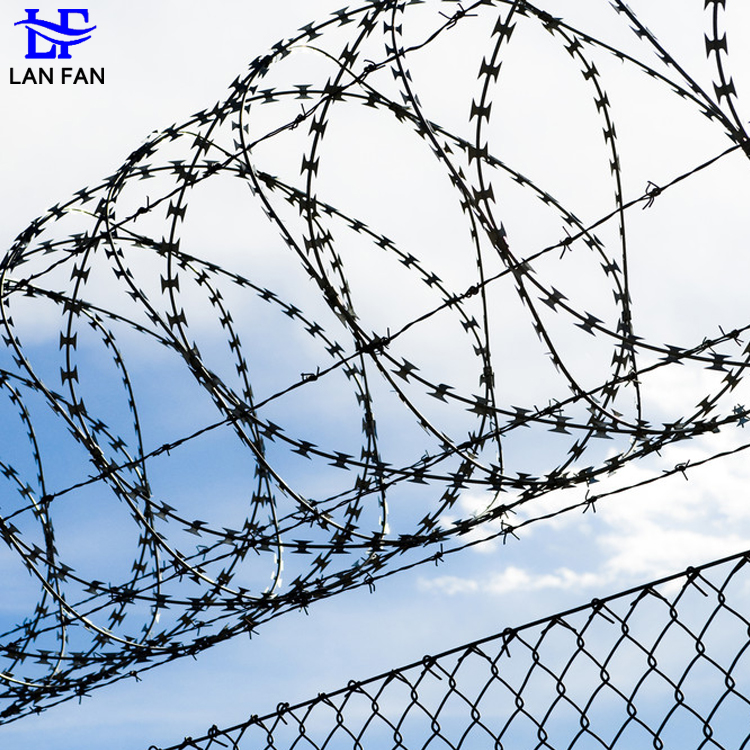
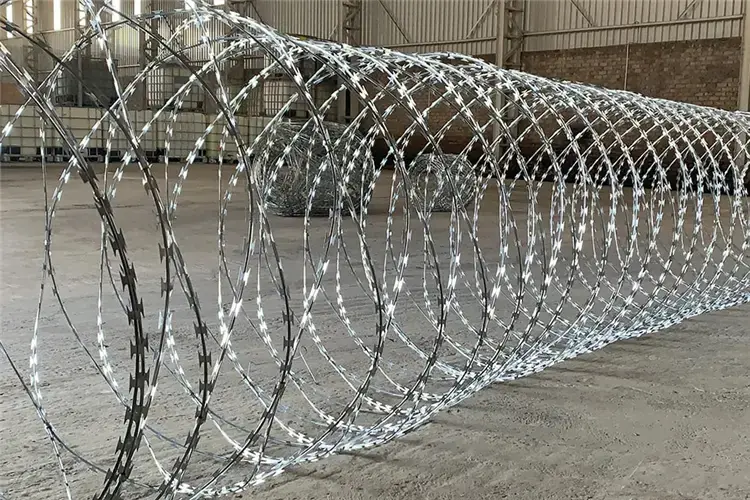
Razor Wire (Barbed Tape / Concertina Wire)
1-Construction
•It's fabricated from galvanized steel strip, mechanically stamped or clipped into continuous sequences of sharp, blade-like segments exhibiting razor edges.
•The blade segments are permanently crimped onto a central core wire or woven between dual core wires, forming a continuous linear or coiled configuration.
•Principal configurations include:
(1). Flat Wrap: Linear tape deployment.
(2). Concertina Coil: Spring-like cylindrical coils designed for expansion into three-dimensional obstacles.
(3). Simple Coil: Non-expanding helical arrangement.
2-Functional Mechanism
•Engineered toinflict significant injury(deep lacerations, severe cuts) upon contact, functioning as animmediate and formidable physical obstruction. Provides aneffective delay mechanismagainst intrusion.
•Offers asuperior deterrent efficacycompared to barbed wire due to the substantially elevated risk of serious trauma.
3-Security Efficacy Against Human Intrusion
•It has high deterrence level. Breach attempts entail considerable risk of incapacitating injury. Protective textiles provide limited defense against the slicing action of the blades. Overcoming this barrier requires specialized equipment, substantial time (imposing delay), or exceptional risk tolerance.
4-Typical Applications
•Perimeter security for high-risk/high-value assets:correctional facilities, military installations, national borders, critical infrastructure (e.g., power generation plants), sensitive government sites, secure storage complexes.
•Deployed where robust physical deterrence and intrusion delay are paramount security requirements.
5-Morphological Characteristics
•It exhibits a banded or ribbon-like profile densely arrayed with sharp, continuous blade elements. Concertina configurations manifest as large, helical coils.
Barbed Wire VS. Razor Wire
|
Item |
Barbed Wire |
Razor Wire |
|
Material |
Steel wire strands with formed barbs |
Galvanized steel strip formed into blades |
|
Edge Configuration |
Discrete barbs:Spaced pointed projections |
Continuous blades:Linear razor-sharp edges |
|
Deterrence Level |
Moderate (minor injury, entanglement) |
High (severe laceration risk) |
|
Intrusion Resistance |
Maybe traversed with effort/acceptance of minor injury |
Extremely difficult/dangerous to breach rapidly |
|
Primary Function |
Delineation & psychological deterrence |
Physical barrier & injury-infliction |
|
Primary Target |
Livestock; low-threat human intrusion |
Determined human intruders |
|
Deployment Context |
Agriculture, low-security sites, barrier topping |
High-security facilities, borders, prisons, military |
|
Visual Profile |
Strands with periodic sharp points |
Ribbon/tape with continuous blades or sharp coils |
|
Breach Methodology |
Relatively feasible (forceful traversal with protection) |
Highly hazardous, necessitating specialized equipment/time |
Conclusion
While both barbed wire and razor wire serve the purpose of securing a boundary, they differ significantly in structure, security level, cost, and use cases. If you need basic protection for livestock or farmland, barbed wire is likely sufficient. However, for high-risk areas where intrusion must be strongly prevented, razor wire is the superior choice.